RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions: Start your Class 9 Maths exam preparation with the RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths. You can always rely on the RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions for your exam prep as well as class assignments. Subject matter experts have designed the solutions of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions in a well-explained way.
Download the RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions Free PDF by using the link given in the blog. To know more, read the whole blog.
Download RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions PDF
RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions
RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions – Overview
In Chapter 13 of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths, you will know many things like line segments using a ruler, compass, protractor, and more. You will learn about the construction of various geometrical shapes and figures, like bisecting angles or lines.
You will also learn about triangle construction with different cases, mentioned below:
- Two lower or base angles are there with the perimeter.
- One of the base angles and differences between any two other sides.
- Length of the base, one of the base angles, and the sum of any two sides.
- There is a single exercise in Chapter 13 with 21 questions in total. These questions are based on different types of construction.
- In the beginning, you have to draw a perpendicular bisector of a particular line.
- Now you have constructions and measurements of an 80-degree angle and then bisect it.
- Then, you have to construct, by only using a ruler and compass, a 90-degree angle, and then bisect it.
- Further, you need to construct triangles with various conditions such as only two angles given or one side and one angle given.
- As you proceed into the chapter, you will study concepts of equilateral and right-angled triangles along with the construction of squares.
Access The RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions
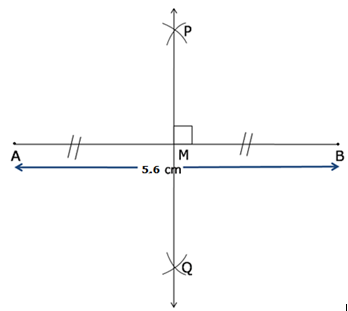
Solution 1
Steps of construction:
- Draw line segment AB = 5.6 cm
- With A as centre and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs, one on each side of AB.
- With B as centre and the same radius as in step 2, draw arcs cutting the arcs drawn in the previous step at P and Q respectively.
- Join PQ to intersect AB at M.
Thus, PQ is the required perpendicular bisector of AB.
AM = BM = 2.8 cm
Solution 2
Steps of construction:
1. Draw ray OB.
2. With the help of protractor construct an angle AOB of measure 80°.
3. With centre O and convenient radius draw an arc cutting sides OA and OB at Q and P respectively.
4. With centre Q and radius more than half of PQ, draw an arc.
5. With centre P and the same radius, as in the previous step, draw another arc intersecting the arc drawn in the previous step at R.
6. Join OR and produce it to form ray OX.
Then, OX is the required bisector of ∠AOB.
∠AOX = ∠BOX = 40°
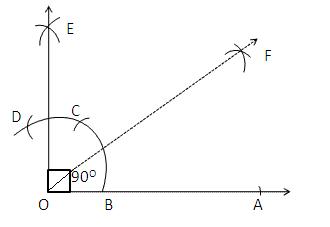
Solution 3
Step of Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment OA.
(ii) With O as centre and any suitable radius draw an arc, cutting OA at B.
(iii) With B as centre and the same radius cut the previously drawn arc at C.
(iv) With C as centre and the same radius cut the arc at D.
(v) With C as centre and the radius more than half CD draw an arc.
(vi) With D as centre and the same radius draw another arc which cuts the previous arc at E.
(vii) Join ENow, AOE =900
(viii) Now with B as centre and radius more than half of CB draw an arc.
(iv) With C as centre and same radius draw an arc which cuts the previousat F.
(x) Join OF.
(xi) F is the bisector of right
AOE.
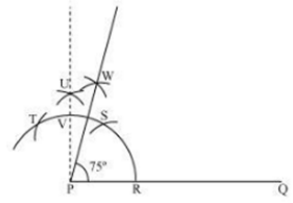
Solution 4(i)
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment PQ.
- With centre P and any radius, draw an arc which intersects PQ at R.
- With centre R and same radius, draw an arc which intersects previous arc at S.
- With centre S and same radius, draw an arc which intersects arc in step 2 at T.
- With centres T and S and radius more than half of TS, draw arcs intersecting each other at U.
- Join PU which intersects arc in step 2 at V.
- With centres V and S and radius more than half of VS, draw arcs intersecting each other at W.
- Join PW.
∠WPQ = 75°
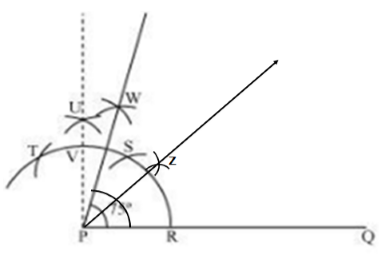
Solution 4(ii)
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment PQ.
- With centre P and any radius, draw an arc which intersects PQ at R.
- With centre R and same radius, draw an arc which intersects previous arc at S.
- With centre S and same radius, draw an arc which intersects arc in step 2 at T.
- With centres T and S and radius more than half of TS, draw arcs intersecting each other at U.
- Join PU which intersects arc in step 2 at V.
- With centres V and S and radius more than half of VS, draw arcs intersecting each other at W.
- Join PW. ∠WPQ = 75°
- Bisect ∠WPQ.
Then, ∠ZPQ = 37.5°
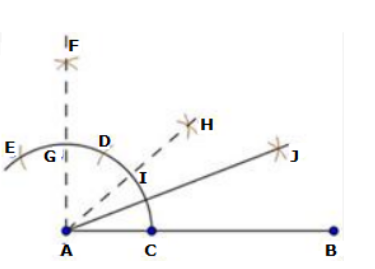
Solution 4(iii)
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment AB and produce BA to point C.
- With centre A and any radius, draw an arc which intersects AC at D and AB at E.
- With centres D and E and radius more than half of DE, draw two arcs which intersect each other at F.
- Join FA which intersects the arc in step 2 at G.
- With centres G and D and radius more than half of GD, draw two arcs which intersect each other at H.
- Join HA.
Then, ∠HAB = 135°
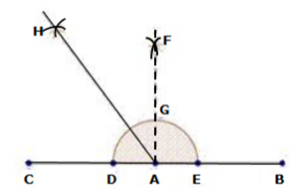
Solution 4(iv)
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment PQ.
- With centre P and any radius, draw an arc which intersects PQ at R.
- With centre R and same radius, draw an arc which intersects previous arc at S.
- With centre S and same radius, draw an arc which intersects arc in step 2 at T.
- With centres T and S and radius more than half of TS, draw arcs intersecting each other at U.
- Join PU which intersects arc in step 2 at V.
- Now taking T and V as centres, draw arcs with radius more than half the length TV.
- Let these arcs intersect each other at W.
- Join PW, which is the required ray making 105°with the given ray PQ.
Then, ∠WPQ = 105°
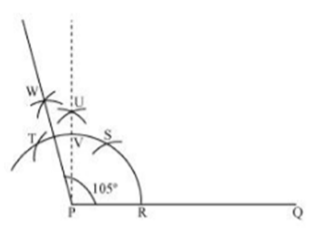
Solution 4(v)
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment AB.
- With centre A and any radius, draw an arc which intersects AB at C.
- With centre C and same radius, draw an arc which intersects previous arc at D.
- With centre D and same radius, draw an arc which intersects arc in step 2 at E.
- With centres E and D and radius more than half of ED, draw arcs intersecting each other at F.
- Join AF which intersects arc in step 2 at G.
- Now taking G and C as centres, draw arcs with radius more than half the length GC.
- Let these arcs intersect each other at H.
- Join AH which intersect the arc n step 2 at I.
- With centres I and C and radius more than half of IC, draw arcs intersecting each other at J.
- Join AJ.
Then, ∠JAB = 22.5°
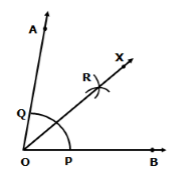
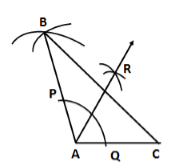
Solution 5
Steps of construction:
- Draw line segment AC = 2.6 cm.
- With A as centre and radius 3.8 cm, draw an arc.
- With C as centre and radius 5 cm, draw arc to intersect the previous arc at B.
- Join AB and BC.
Thus, ΔABC is the required triangle.
Largest side = BC = 5 cm
⇒ Largest angle = ∠A
Steps of construction:
- With A as centre and any radius, draw an arc, which intersect AB at P and AC at Q.
- With P as centre and radius more than half of PQ, draw an arc.
- With Q as centre and the same radius, draw an arac to intersect the previous arc at R.
- Join AR and extend it.
Thus, ∠A is bisected by ray AR.
Solution 6
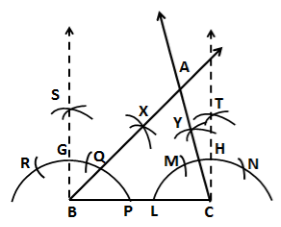
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment BC = 4.8 cm.
- With centre B and any radius, draw an arc which intersects BC at P.
- With centre P and same radius, draw an arc which intersects previous arc at Q.
- With centre Q and same radius, draw an arc which intersects arc in step 2 at R.
- With centres R and Q and radius more than half of RQ, draw arcs intersecting each other at S.
- Join BS which intersects arc in step 2 at G. Then, ∠SBC = 90°
- With centre P and radius more than half of PG, draw an arc.
- With centre G and same radius, draw an arc which intersects previous arc at X.
- Join B and extend it. Then ∠B = 45°
- Construct ∠TCB = 90° following the steps given above.
- With centres M and H and radius more than half of MH, draw arcs intersecting each other at Y.
- Join CY and extend it. Then, ∠C = 75°
- Extended BX and CY intersect at A.
Thus, ΔABC is the required triangle.
m∠A = 60°
Solution 7
Step of construction:
(i) Draw a line segment BC=5cm.
(ii) With B as centre and radius equal to BC draw an arc.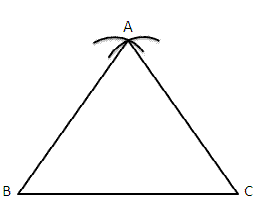
Solution 8
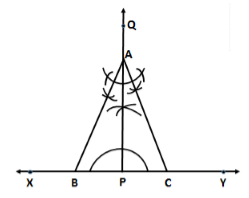
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line XY.
- Mark any point P on it.
- From P, draw PQ ⊥ XY.
- From P, set off PA = 5.4 cm, cutting PQ at A.
- Construct ∠PAB = 30° and ∠PAC = 30°, meeting XY at B and C respectively.
Then, ABC is the required equilateral triangle.
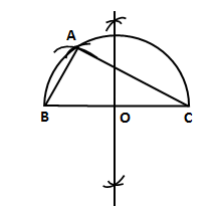
Solution 9
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment BC = 5 cm.
- Find the midpoint O of BC.
- With O as centre and radius OB, draw a semicircle on BC.
- With B as centre and radius equal to 4.5 cm, draw an arc, cutting the semicircle at A.
- Join AB and AC.
Then, ΔABC is the required triangle.
Solution 10
Steps of construction:
- Draw BC = 4.5 cm
- Draw ∠CBX = 45°
- From ray BX, cut-off line segment BD equal to AB + AC, i.e. 8 cm.
- Join CD.
- Draw the perpendicular bisector of CD meeting BD at A.
- Join CA to obtain the required triangle ABC.
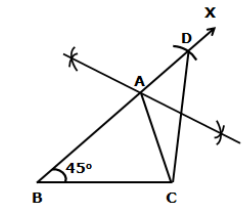
Justification:
Clearly, A lies on the perpendicular bisector of CD.
∴ AC = AD
Now, BD = 8 cm
⇒ BA + AD = 8 cm
⇒ AB + AC = 8 cm
Hence, ΔABC is the required triangle.
Solution 11
Steps of construction:
- Draw AB = 5.8 cm
- Draw ∠ABX = 60°
- From ray BX, cut off line segment BD = BC + CA = 8.4 cm.
- Join AD.
- Draw the perpendicular bisector of AD meeting BD at C.
- Join AC to obtain the required triangle ABC.
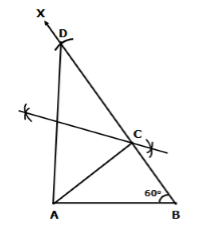
Justification:
Clearly, C lies on the perpendicular bisector of AD.
∴ CA = CD
Now, BD = 8.4 cm
⇒ BC + CD = 8.4 cm
⇒ BC + CA = 8.4 cm
Hence, ΔABC is the required triangle.
Solution 12
Steps of construction:
- Draw base BC = 6 cm
- Construct ∠CBX = 30°
- From ray BX, cut off line segment BD = 3.5 cm (= AB – AC)
- Join CD.
- Draw the perpendicular bisector of CD which cuts BX at A.
- Join CA to obtain the required triangle ABC.
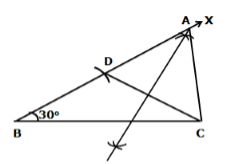
Justification:
Since A lies on the perpendicular bisector of CD.
∴ AD = AC
Now, BD = 3.5 cm
⇒ AB – AD = 3.5 cm
⇒ AB – AC = 3.5 cm
Hence, ΔABC is the required triangle.
Solution 13
Steps of construction:
- Draw base AB = 5 cm
- Construct ∠BAX = 30°
- From ray AX, cut off line segment AD = 2.5 cm (= AC – BC)
- Join BD.
- Draw the perpendicular bisector of BD which cuts AX at C.
- Join BC to obtain the required triangle ABC.
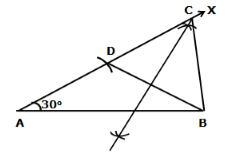
Justification:
Since C lies on the perpendicular bisector of BD.
∴ CD = BC
Now, AD = 2.5 cm
⇒ AC – CD = 2.5 cm
⇒ AC – BC = 2.5 cm
Hence, ΔABC is the required triangle.
Solution 14
Solution 15
Steps of Construction:
- Draw a line segment PQ = 10.4 cm.
- Construct a 45° angle and bisect it to get ∠NPQ.
- Construct a 120° angle and bisect it to get ∠MQP.
- Let the rays PN and QM intersect at A.
- Construct the perpendicular bisectors of PA and QA, to intersect PQ at B and C respectively.
- Join AB and AC.
So, ΔABC is the required triangle.
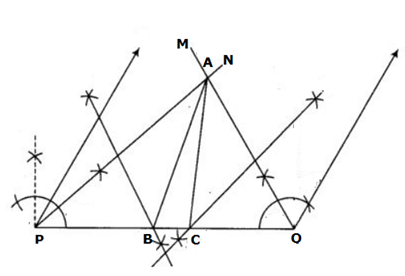
Solution 16
Steps of Construction:
- Draw a line segment PQ = 11.6 cm.
- Construct a 45° angle and bisect it to get ∠NPQ.
- Construct a 60° angle and bisect it to get ∠MQP.
- Let the rays PN and QM intersect at A.
- Construct the perpendicular bisectors of PA and QA, to intersect PQ at B and C respectively.
- Join AB and AC.
So, ΔABC is the required triangle.
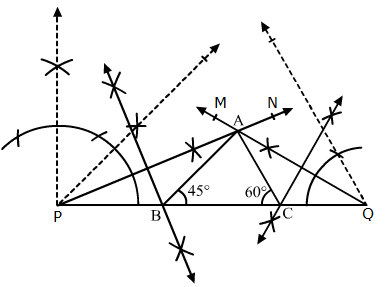
Solution 17(i)
Given,
AB = 6 cm, ∠A = 40° and (BC + AC) = 5.8 cm
We know that the sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
Here, we find that BC + AC < AB
Hence, construction of triangle ABC with given measurements is not possible.
Solution 17(ii)
Given,
AB = 7 cm, ∠A = 50° and (BC – AC) = 8 cm
We know that the sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
That is,
AB + AC > BC
⇒ AB + AC – AC > BC – AC
⇒ AB > BC – AC
Here, we find that AB < BC – AC
Hence, construction of triangle ABC with given measurements is not possible.
Solution 17(iii)
Given,
BC = 5 cm, ∠B = 80°, ∠C = 50° and ∠A = 60°
We know that the sum of the measures of three angles of a triangle is 180°.
Here, we find that
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 60° + 80° + 50° = 190° > 180°
Hence, construction of triangle ABC with given measurements is not possible.
Solution 17(iv)
Given,
AB = 4 cm, BC = 3 cm and AC = 7 cm
We know that the sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
Here, we find that AB + BC = AC
Hence, construction of triangle ABC with given measurements is not possible.
Solution 18
Steps for Construction:
1. Draw a line XY.
2. Take a point A on XY.
3. With A as the centre, draw a semi-circle, cutting XY at P and Q.
4. Construct ∠YAC = 90°.
5. Draw the bisector AB of ∠XAC. Then ∠YAB = 135°.
6. Draw the bisector AM of ∠YAB. Then ∠YAM = 67.5°.
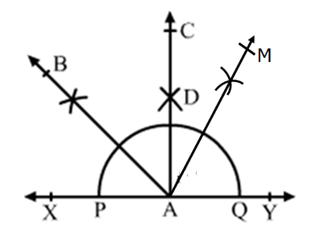
Solution 19
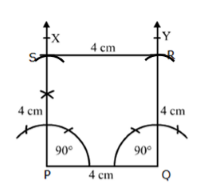
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment PQ = 4 cm.
2. Construct ∠QPX = 90° and ∠PQY = 90°.
3. Cut an arc PS = 4 cm and QR = 4 cm. Join SR.
So, PQRS is the required square.
Solution 20
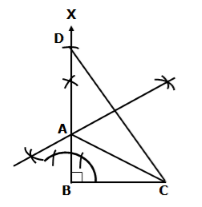
Steps of construction:
- Draw BC = 3.5 cm
- Draw ∠CBX = 90°
- From ray BX, cut off line segment BD = AB + AC = 5.5 cm.
- Join CD.
- Draw the perpendicular bisector of CD meeting BD at A.
- Join AC to obtain the required triangle ABC.
Solution 21
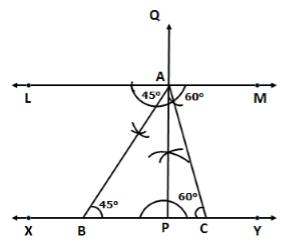
Steps of construction:
- Draw any line XY.
- Take any point P on XY and draw PQ ⊥ XY.
- Along PQ, set off PA = 4.5 cm.
- Through A, draw LM ∥ XY.
- Construct ∠LAB = 45° and ∠MAC = 60°, meeting XY at B and C respectively.
Then, ΔABC is the required triangle.
FAQs on RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions
From where can I find the download link for the RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions PDF?
You can find the download link of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions PDF in the above blog.
How much does it cost to download the RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions PDF?
You can download RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions PDF for free.
Can I access the RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Geometrical Constructions PDF Offline?
Once you have downloaded the RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 – Geometrical Constructions PDF online, you can access it offline whenever you want.
Is the RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 – Geometrical Constructions PDF a credible source for Class 9 Maths exam preparation?
Yes, the solutions of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 – Geometrical Constructions are prepared by the subject matter experts, hence credible.
How many exercises are there in RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13?
There is only one exercise in this chapter.
How many questions are there in RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 13 Ex 13.1?
There are 21 questions in this exercise.